CO and CO2 - What's the Difference?
2nd Jan 2024
Too often CO and CO2 are mistaken for one another as they are both colorless and odorless. It's important to recognize the difference.
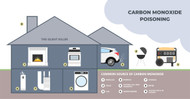
Carbon Monoxide (CO) aka the "Silent Killer"
- Does not occur naturally in the atmosphere
- Result of incomplete combustion from carbon-based compounds (ex. coal, natural gas, propane, oil, wood, etc.)
- Automobile internal combustion engines are the largest source of CO
- Flammable Gas that is slightly lighter than air
- Common Type of fatal poisoning
-
- Symptoms: dizziness, headache, nausea, shortness of breath, confusion, blurred vision, loss of consciousness
- Target Organs: lungs, blood, heart, central nervous system
- OSHA Standards: Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) 50 PPM
- NIOSH Standards: Recommend Exposure Limit (REL) 35 PPM
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Acrid Taste
- Occurs naturally in the atmosphere at about 400 PPM
- Formed by human and animal respiratory cycle as well as combustion
- Used for beverage carbonation and plant growth acceleration
-
- Unsafe levels can build up in normally occupied areas because of poor ventilation
- Non-flammable gas that is heavier than air
- Poisoning is rare
- Symptoms: increased heart rate, frostbite, panic, convulsion, impaired consciousness
- Target Organs: respiratory system, cardiovascular system
- OSHA Standards: PEL 5,000 PPM
- NIOSH Standards: REL 5,000 PPM
Common Applications Where BOTH Gases Could Be Present
Parking Garages – Vehicle Repair Facility – Automobile Exhaust – Food Processing – Chemical Plants – Food & Beverage – Office Buildings – Bus Depots – Schools – Restaurants – Retail – Maintenance Facility – Grow Facilities- Manufacturing Plants – Confined Spaces – Wastewater Treatment – Pharmaceuticals – Fast Food Establishments
TG Technical Services can provide the product for your gas detection and monitoring needs!